- Kolshet Diagnostics & Oscar Hospital, Thane.
- ankit17593@gmail.com
- +91 7588000111
- Mon to Sat: 10am to 9pm
Tracheostomy Treatment
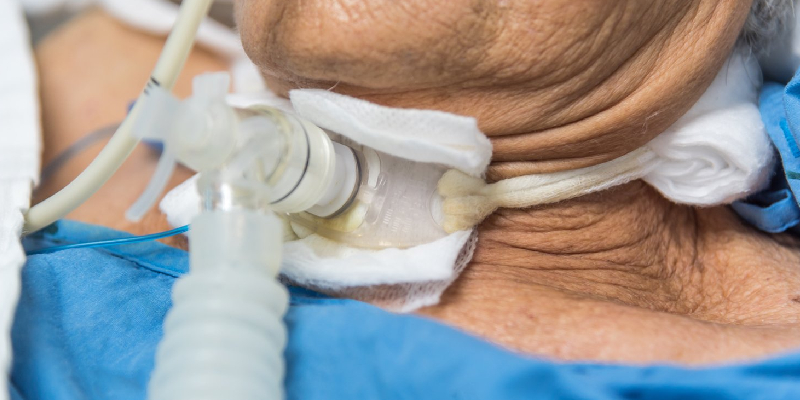
Tracheostomy Treatment in Thane
At our clinic in Kolshet, we offer expert Tracheostomy treatment in Thane performed by Dr. Ankit Singh, a leading ENT specialist in Kolshet with years of experience in airway procedures. This life-saving procedure is performed to assist patients who are unable to breathe normally due to airway blockages or require long-term ventilation.
A Tracheostomy involves creating an opening in the trachea (windpipe) to bypass upper airway obstructions. This allows the patient to breathe comfortably and safely. Depending on the patient’s condition, the procedure can be either temporary or permanent. Our clinic ensures that the procedure is conducted with the highest level of care, safety, and precision.
Dr. Ankit Singh has successfully handled numerous cases of Tracheostomy treatment in Thane, providing personalized post-operative care and support to each patient. As an ENT specialist in Kolshet, his goal is to ensure patient comfort, quick recovery, and restored quality of life.
Book an Appointment
To know whether you or your loved one may benefit from Tracheostomy treatment in Thane, please contact Dr. Ankit Singh or call us directly at +91 75880 00111. As a trusted ENT specialist in Kolshet, Dr. Singh is here to guide you every step of the way.
